Effective Care & Treatment for Pressure Sores
Learn evidence-based methods to treat and manage pressure sores and ulcers effectively.
Understanding Pressure Sore Prevention
3 Key Points To Remember:
The primary goals are:
pain management
wound healing
infection prevention
Early intervention is critical to avoid complications.
Treatment strategies vary based on the stage and severity of the sore.
Treatment Options by Severity
-
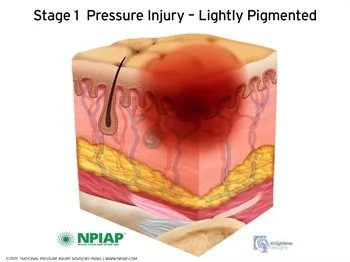
Stage 1 (Mild Redness & Irritation)
• Keep skin clean and dry.
• Use moisture barrier creams.
• Adjust positioning frequently.
• Consider soft silicone dressings for prevention.
-
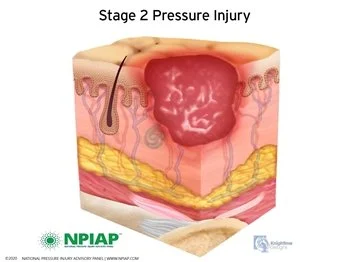
Stage 2 (Blistering or Open Sore)
• Use hydrocolloid or foam dressings.
• Keep the area protected and clean.
• Apply non-adherent wound dressings.
-
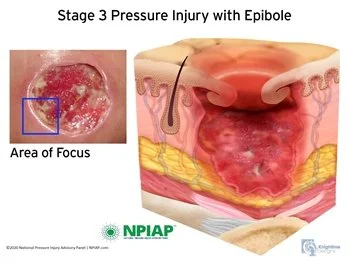
Stage 3 (Deep Wound with Tissue Loss)
• Apply moisture-retaining dressings.
• Use prescribed antimicrobial treatments.
• Consider negative pressure wound therapy.
-
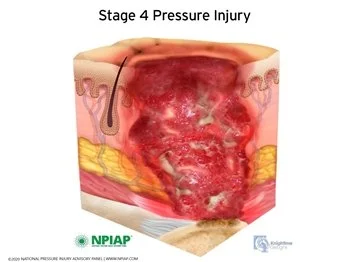
Stage 4 (Exposed Muscle or Bone)
• Requires specialized wound care.
• Possible surgical intervention.
• High risk for infection and osteomyelitis.
Nutritional Support for Healing
The role of diet in wound healing.
-
Supports skin repair and tissue rebuilding.
-
Boosts collagen formation.
-
Prevents skin breakdown.
Wound Care & Pain Management Strategies
-

Wound Care Strategies
Step-by-step guide for caregivers on treating pressure sores at home.
Cleansing & Debridement
• Use saline or antimicrobial solutions for cleaning.
• Avoid harsh chemicals like hydrogen peroxide.
Infection Control
• Watch for signs of infection (heat, swelling, increased pain).
• Use prescribed topical antibiotics if necessary.
Dressing Selection
• Foam Dressings: For moderate wounds.
• Hydrocolloid Dressings: For moisture retention.
• Antimicrobial Dressings: For infected wounds.
-

Pain Management
Addressing discomfort and improving quality of life.
Non-Pharmacological Methods
• Repositioning techniques
• Cooling pads and pressure relief cushions
Topical Pain Relief
• Lidocaine gels or numbing sprays
Medication Options
• OTC pain relievers (**Ibuprofen, Acetaminophen**)
• Prescription painkillers in severe cases
Medical & Surgical Intervention
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy
Uses suction to remove fluid and promote healing.
Surgical Debridement
Removes infected or dead tissue.
Flap Surgery
Covers deep wounds with healthy skin from another area.
Contact Us
Set up a free consultation to discuss your pressure sore journey or that of your loved one, please use our online form, and a member of our team will get back to you shortly.



